Welcome to the world of Bitcoin, where digital currency transforms how we think about finance and economics. A critical event in this realm is the Bitcoin Halving, a process that not only fascinates crypto enthusiasts but also plays a pivotal role in the currency’s value and scarcity. In this guide, we’ll demystify the Bitcoin Halving and explore its significance in the cryptocurrency landscape.
What is Bitcoin Halving?
Bitcoin Halving is an event that occurs approximately every four years, wherein the reward for mining new Bitcoin blocks is halved. This means miners receive 50% less Bitcoin for verifying transactions. This mechanism is part of Bitcoin’s design to control inflation by reducing the rate of new Bitcoin entering circulation.
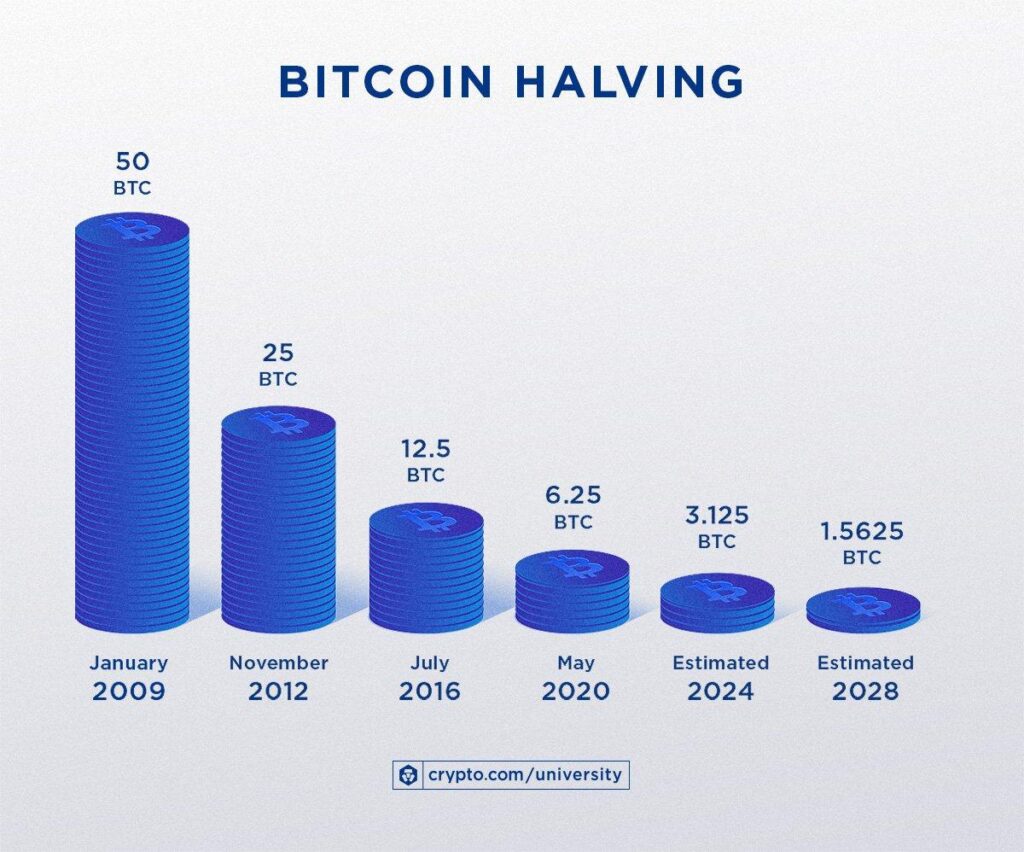
The halving is significant because it directly influences Bitcoin’s supply. With fewer new Bitcoins generated, the scarcity can lead to an increase in Bitcoin’s price, assuming demand remains steady or increases.
The halving is significant because it directly influences Bitcoin’s supply. With fewer new Bitcoins generated, the scarcity can lead to an increase in Bitcoin’s price, assuming demand remains steady or increases.
One of the most crucial aspects of Bitcoin Halving is its role in controlling inflation. Unlike traditional fiat currencies, which can be printed endlessly, Bitcoin has a capped limit of 21 million coins. Halving is the process that helps regulate the speed at which new Bitcoins are created and released into circulation, ensuring that this cap is not reached too quickly. This built-in scarcity is similar to precious metals like gold, which cannot be easily increased to meet rising demand.
The halving event often leads to significant speculation and interest in the Bitcoin market. Historically, halvings have been associated with substantial price increases. The logic behind this is simple: as the rewards for mining decrease, the supply growth of new Bitcoins slows down. If demand remains constant or increases, the reduced supply growth can lead to higher prices. However, it’s important to note that markets are influenced by a multitude of factors, and halving is just one of them. This chart illustrates how Bitcoin’s price has historically reacted to halving events.
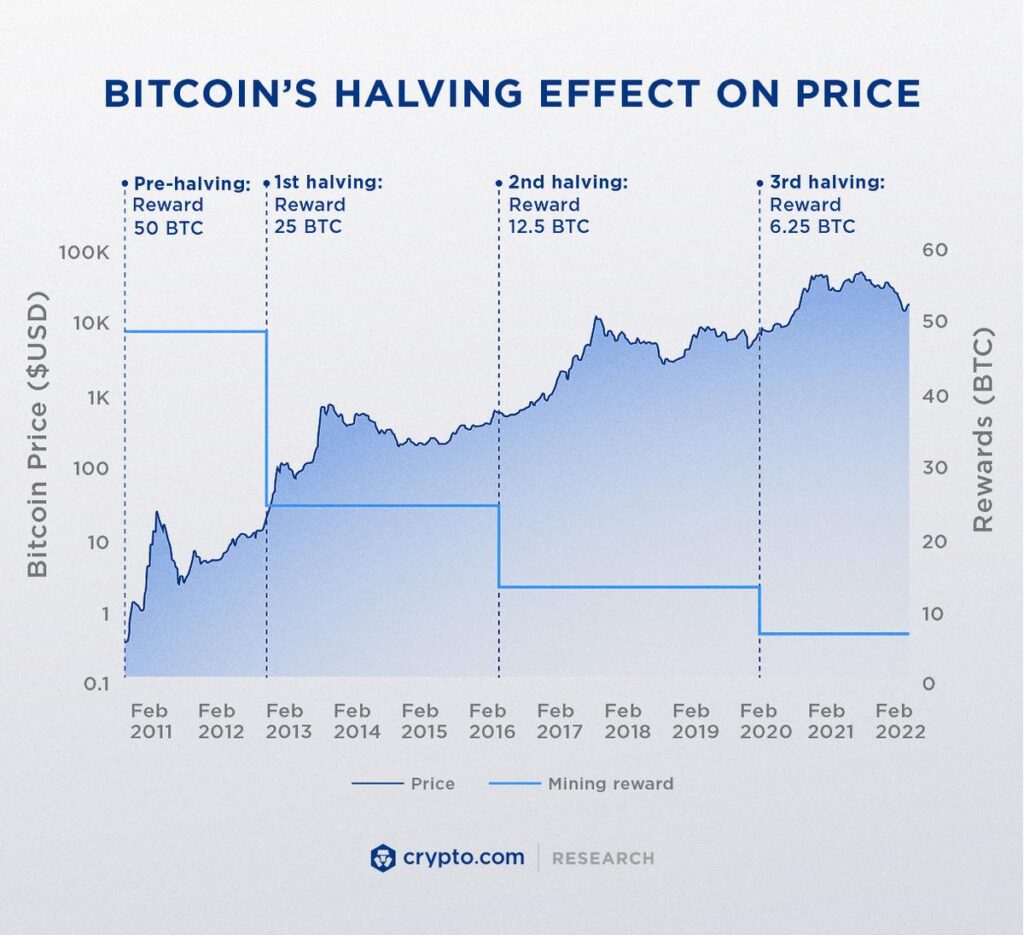
For investors, understanding the implications of Bitcoin Halving is crucial. It’s a reminder of the importance of long-term thinking in cryptocurrency investment.
Long-Term Effects on the Ecosystem
The long-term effects of halving extend beyond immediate price implications. As mining rewards diminish, the incentive structure for miners changes. This can impact the security and decentralization of the Bitcoin network. Miners are incentivized to maintain the network’s security through their mining activities, and reduced rewards could influence their operations. However, if the price of Bitcoin increases sufficiently, it can offset the reduced block reward, maintaining the economic viability of mining.
To understand the potential impact of future halvings, it’s useful to look at past events. Each previous halving has had its unique context and market conditions, resulting in different outcomes. For instance, the first halving in 2012 saw a gradual but significant increase in Bitcoin’s price over the following year. The 2016 halving followed a similar pattern, though the price increase was more pronounced. The 2020 halving occurred amidst a different global economic landscape, influenced by factors like the COVID-19 pandemic, leading to unique market reactions.
For investors, understanding the implications of Bitcoin Halving is crucial. It’s a reminder of the importance of long-term thinking in cryptocurrency investment. Halving events highlight the unique economic model of cryptocurrencies and provide opportunities for investors to evaluate their investment strategies in light of these cyclical events.
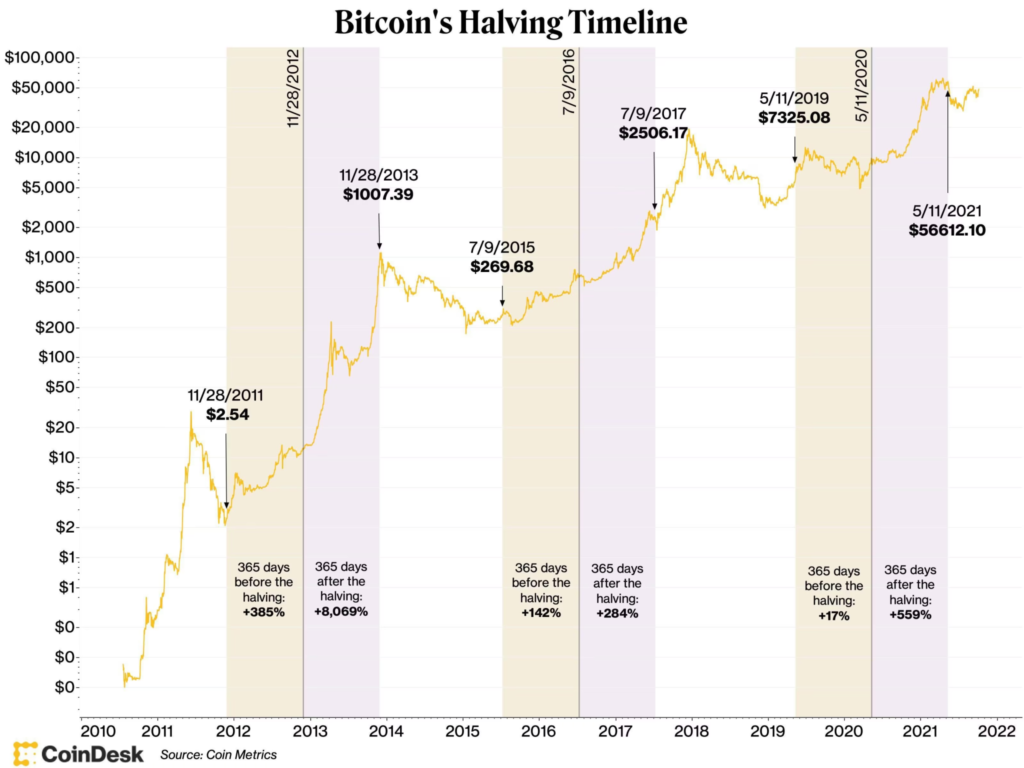
Halving Events and Price Correlation:
- First Halving (11/28/2012):
- 365 days before halving: Price was approximately $2.54, and it experienced a substantial increase of +385% leading up to the halving.
- 365 days after halving: The price saw an astronomical rise to about $1,007.39, which is an increase of +8,069% from the pre-halving price.
- Second Halving (7/9/2016):
- 365 days before halving: Price was around $269.68, with a notable increase of +142% leading up to the halving.
- 365 days after halving: The post-halving year witnessed a rise to roughly $2,506.17, marking an increase of +284%.
- Third Halving (5/11/2020):
- 365 days before halving: The price leading up to this event was $7,325.08, with a modest increase of +17% from one year before.
- 365 days after halving: The price escalated to around $56,612.10, indicating a significant gain of +559%.
General Observations:
- Increasing Baseline Prices: Each halving event starts from a higher baseline price than the previous one, illustrating the overall upward trend in Bitcoin’s price over the years.
- Diminishing Relative Gains Post-Halving: While the absolute price increases significantly after each halving, the percentage gain post-halving shows a decreasing trend. From over 8,000% after the first halving, it’s down to 559% after the third.
- Price Stability Post-Halving: The chart suggests that while there’s a lot of volatility before and shortly after the halving, prices seem to stabilize or continue to rise at a steadier rate as the market adjusts to the new supply dynamics.
- Halving as a Potential Indicator: The chart implies that halving events may be used as indicators for significant price movements, though it should be noted that correlation does not necessarily imply causation.
Market Sentiment and Speculation:
- Pre-Halving Hype: There appears to be a trend of increasing prices leading up to the halving, which may be attributed to speculation and investors buying in anticipation of potential price increases.
- Post-Halving Realization: After each halving, the reality of reduced supply seems to have a delayed effect on the price, leading to significant gains in the following year.
Conclusion:
The chart presents Bitcoin halvings as potentially bullish events that reduce the pace at which new bitcoins are generated, leading to a decrease in supply growth. Historically, this has corresponded with substantial price increases, though the degree of impact seems to be diminishing with each successive halving.
This historical perspective is valuable for investors considering the implications of future halvings. However, it’s also essential to recognize that many other factors can affect Bitcoin’s price, and past performance is not always indicative of future results. The crypto market has matured over the years, and each halving occurs in a different macroeconomic environment, with varying investor sentiments and market dynamics.
Additional Resources
For more in-depth information, check out these resources:






